The Burden of Dysentery
Dysentery is a significant public health concern, particularly in developing countries with poor sanitation and hygiene infrastructure. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), dysentery affects approximately 165 million people worldwide each year, resulting in over 1.1 million deaths. The disease is most prevalent in areas with inadequate access to clean water, proper sewage disposal, and healthcare facilities. Children under the age of 15 are disproportionately affected, with dysentery being a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in this age group.
Public Health Campaigns: A Proactive Approach
Public health campaigns have been instrumental in preventing the spread of dysentery and promoting healthy practices in communities. These campaigns aim to educate the public about the causes, symptoms, and prevention of dysentery, as well as the importance of proper hygiene and sanitation. The key strategies employed by public health campaigns include:
- Health Education: Public health campaigns disseminate information about dysentery through various channels, including print and electronic media, community outreach programs, and school-based initiatives. Health education materials are designed to be culturally sensitive and linguistically accessible to ensure that the message reaches all segments of the population.
- Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Promotion: Public health campaigns emphasize the importance of proper WASH practices, including handwashing with soap, using latrines, and accessing clean water. These practices are crucial in preventing the spread of dysentery and other waterborne diseases.
- Food Safety: Public health campaigns promote safe food handling practices, including proper food storage, handling, and cooking techniques. This helps to prevent the contamination of food and water with Shigella bacteria.
- Vaccination: Public health campaigns also promote vaccination against dysentery, particularly in areas with high incidence rates. Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent the disease, and campaigns aim to increase vaccination coverage among high-risk populations.
Examples of Successful Public Health Campaigns
Several public health campaigns have been successful in preventing the spread of dysentery and promoting healthy practices in communities. For example:
- The Global Handwashing Day Campaign: Launched by the WHO and UNICEF, this campaign aims to promote handwashing with soap as a key prevention strategy against dysentery and other infectious diseases.
- The WASH Campaign: Implemented by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), this campaign focuses on improving WASH practices in developing countries, including the construction of latrines and promotion of handwashing with soap.
- The Dysentery Prevention Campaign: Launched by the government of Bangladesh, this campaign aims to reduce the incidence of dysentery through health education, WASH promotion, and vaccination.
Challenges and Opportunities
While public health campaigns have been effective in preventing the spread of dysentery, several challenges remain. These include:
- Limited Resources: Public health campaigns often face limited funding, which can hinder their reach and impact.
- Cultural and Social Barriers: Public health campaigns must navigate cultural and social barriers to ensure that health messages are accessible and acceptable to all segments of the population.
- Infrastructure Constraints: In areas with poor sanitation and hygiene infrastructure, public health campaigns must work to improve these facilities to prevent the spread of dysentery.
Despite these challenges, public health campaigns offer several opportunities for preventing the spread of dysentery. These include:
- Community Engagement: Public health campaigns can engage communities in dysentery prevention efforts, promoting a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Public health campaigns can forge partnerships with local organizations, governments, and international agencies to leverage resources and expertise.
- Innovative Technologies: Public health campaigns can utilize innovative technologies, such as mobile health platforms and social media, to disseminate health messages and promote healthy practices.
FAQs
- What is dysentery, and how is it spread?
Dysentery is a highly infectious disease caused by the ingestion of food and water contaminated with the bacteria Shigella. It can spread through contaminated food and water, as well as through person-to-person contact. - How can I prevent dysentery?
To prevent dysentery, practice proper hygiene and sanitation, including handwashing with soap, using latrines, and accessing clean water. Additionally, ensure that food is handled, stored, and cooked safely. - What are the symptoms of dysentery?
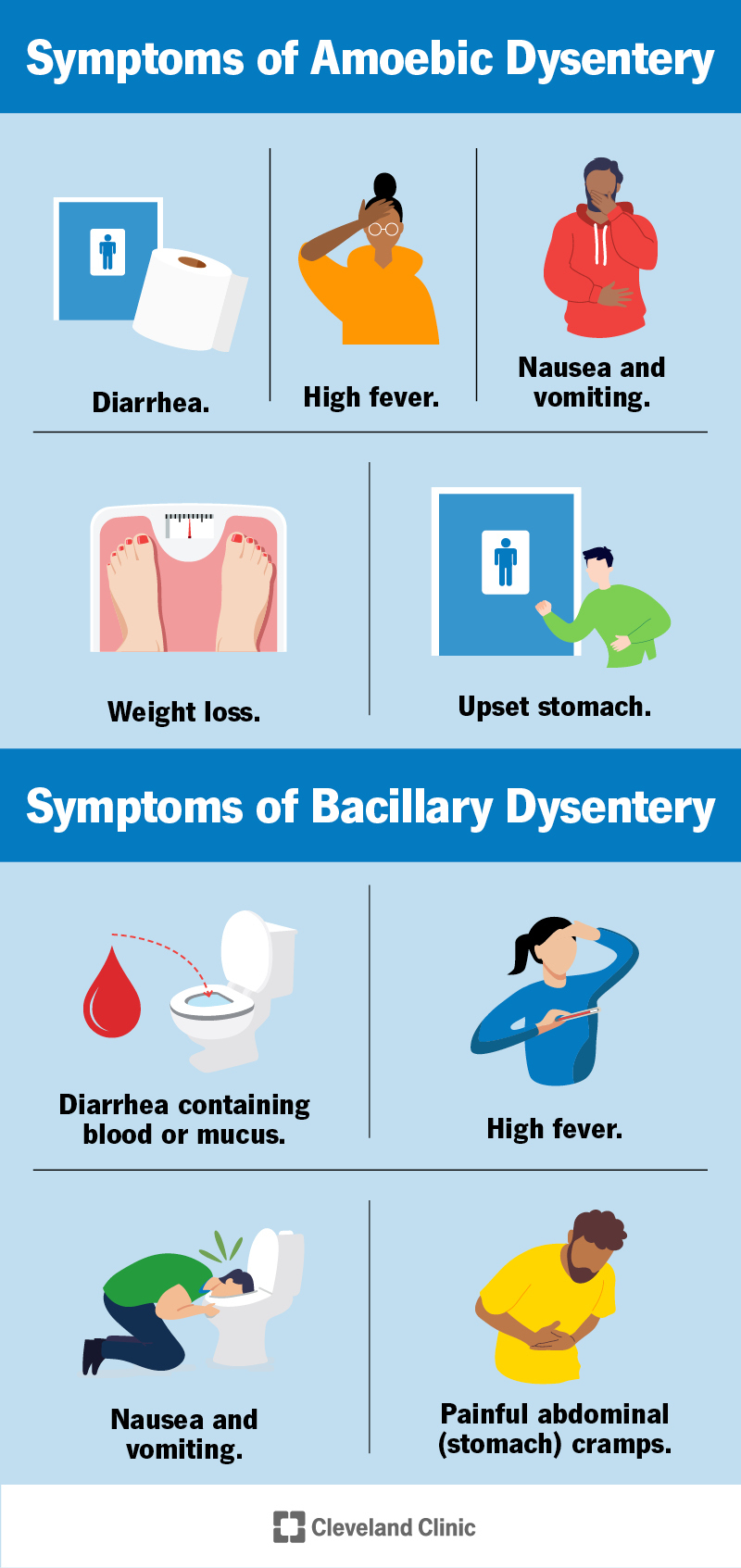
The symptoms of dysentery include severe diarrhea, stomach cramps, fever, and vomiting. If left untreated, dysentery can lead to dehydration, malnutrition, and even death. - Is there a vaccine for dysentery?
Yes, there are vaccines available for dysentery, particularly in areas with high incidence rates. Vaccination is a highly effective way to prevent the disease. - How can I get involved in dysentery prevention efforts?
You can get involved in dysentery prevention efforts by participating in public health campaigns, promoting healthy practices in your community, and supporting organizations working to improve sanitation and hygiene infrastructure.
Conclusion
Dysentery prevention public health campaigns are a crucial step towards promoting healthy practices and preventing the spread of this highly infectious disease. By educating the public about the causes, symptoms, and prevention of dysentery, these campaigns can help to reduce the incidence of the disease and improve community health. While challenges remain, public health campaigns offer several opportunities for preventing the spread of dysentery, including community engagement, partnerships and collaborations, and innovative technologies. By working together, we can create a healthier and more sustainable future for all.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention public health campaigns. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!