Causes and Risk Factors of Dysentery
Dysentery is primarily caused by the bacteria Shigella, which is spread through contaminated food, water, and poor hygiene practices. In urban slums, the risk of contracting dysentery is high due to the following factors:
- Inadequate sanitation: The lack of proper toilet facilities and waste management systems leads to the contamination of soil, water, and air, creating an environment conducive to the spread of dysentery.
- Poor hygiene practices: The absence of basic hygiene practices, such as handwashing with soap and water, facilitates the spread of the disease.
- Contaminated water sources: Urban slums often rely on untreated or contaminated water sources, which can harbor the bacteria that cause dysentery.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition, common in urban slums, can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including dysentery.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing dysentery in urban slums requires a multi-faceted approach that involves community-based initiatives, effective waste management, and access to clean water and sanitation. Some effective prevention strategies include:
- Improving access to clean water and sanitation: Providing access to clean water and sanitation facilities, such as toilets and latrines, can significantly reduce the risk of dysentery.
- Promoting hygiene practices: Educating communities about the importance of handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the toilet and before eating, can prevent the spread of dysentery.
- Implementing effective waste management systems: Proper waste collection, disposal, and treatment can prevent the contamination of soil, water, and air, reducing the risk of dysentery.
- Providing nutrition education: Educating communities about the importance of proper nutrition and providing access to nutritious food can help prevent malnutrition and strengthen the immune system.
Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives play a crucial role in preventing dysentery in urban slums. Some effective community-based initiatives include:
- Community-led total sanitation (CLTS): CLTS is an approach that involves community members in the planning, implementation, and maintenance of sanitation facilities, promoting a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Hygiene promotion: Community-based hygiene promotion programs can educate individuals about the importance of handwashing with soap and water, proper waste disposal, and other hygiene practices.
- Water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) committees: WASH committees, composed of community members, can oversee the management of water and sanitation facilities, ensuring that they are properly maintained and functioning.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the importance of preventing dysentery in urban slums, several challenges and limitations exist, including:
- Limited access to resources: Urban slums often lack the resources, including funding, infrastructure, and personnel, needed to implement effective prevention strategies.
- Cultural and social barriers: Cultural and social barriers, such as the lack of awareness about the importance of hygiene practices, can hinder the adoption of prevention strategies.
- Inadequate governance: Inadequate governance and lack of coordination among stakeholders can hinder the implementation of effective prevention strategies.
FAQs
- What is dysentery, and how is it spread?
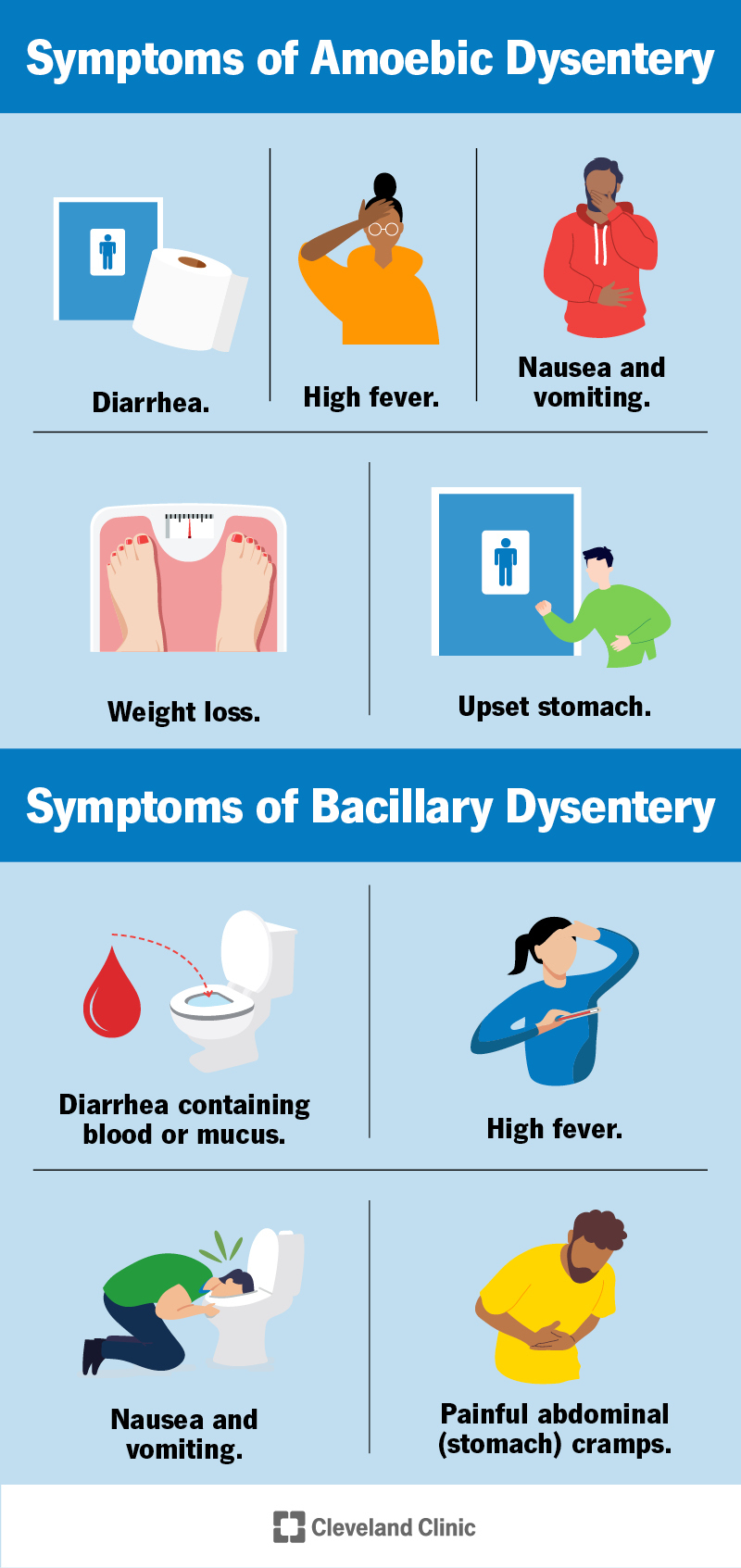
Dysentery is a diarrheal disease caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections. It is spread through contaminated food, water, and poor hygiene practices. - What are the symptoms of dysentery?
The symptoms of dysentery include bloody stools, fever, and abdominal pain. - How can dysentery be prevented?
Dysentery can be prevented by improving access to clean water and sanitation, promoting hygiene practices, implementing effective waste management systems, and providing nutrition education. - What is the role of community-based initiatives in preventing dysentery?
Community-based initiatives, such as community-led total sanitation and hygiene promotion, play a crucial role in preventing dysentery by promoting a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members. - What are the challenges and limitations of preventing dysentery in urban slums?
The challenges and limitations of preventing dysentery in urban slums include limited access to resources, cultural and social barriers, and inadequate governance.
Conclusion
Preventing dysentery in urban slums requires a comprehensive approach that involves community-based initiatives, effective waste management, and access to clean water and sanitation. While challenges and limitations exist, the importance of preventing dysentery cannot be overstated. By working together, governments, NGOs, and community members can implement effective prevention strategies, reducing the risk of dysentery and promoting a healthier community. It is essential to prioritize the prevention of dysentery in urban slums, as it is a crucial step towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). By taking proactive measures to prevent dysentery, we can create a healthier, more equitable, and sustainable future for all.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention in urban slums. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!