Causes and Symptoms of Dysentery
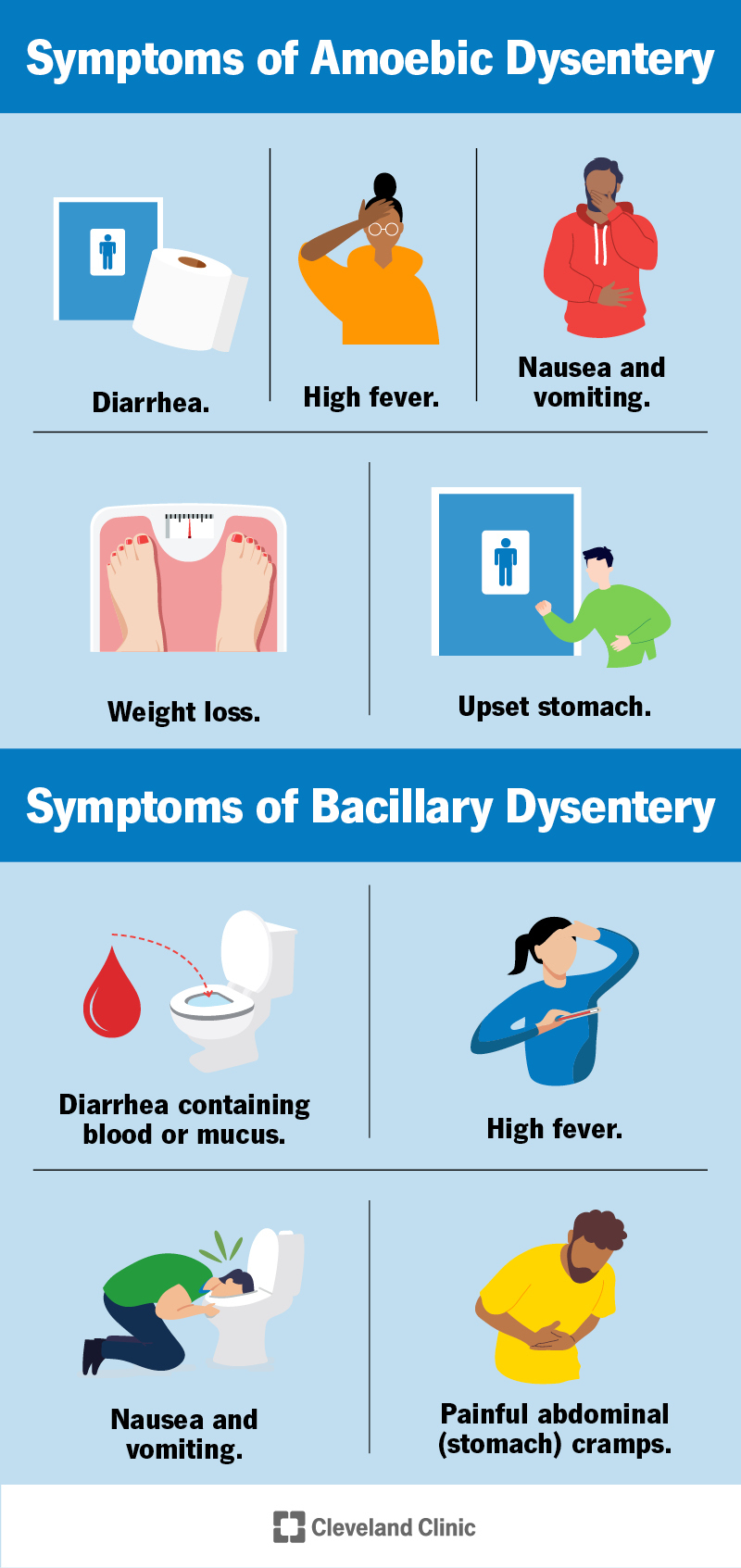
Dysentery is caused by the bacterium Shigella, which is typically spread through the fecal-oral route. The disease can also be caused by other bacteria, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, as well as by parasites like Giardia and Cryptosporidium. The symptoms of dysentery include:
- Diarrhea, often bloody
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
If left untreated, dysentery can lead to severe complications, such as dehydration, malnutrition, and even death.
Dysentery Prevention in Post-Outbreak Areas
Preventing dysentery in post-outbreak areas requires a multi-faceted approach that involves both individual and community-level efforts. Here are some effective ways to prevent dysentery in post-outbreak areas:
- Improve Sanitation and Hygiene: Proper disposal of human waste and provision of clean drinking water are essential to prevent the spread of dysentery. Communities should establish safe and functional latrines, and ensure that all waste is disposed of properly.
- Promote Handwashing: Handwashing with soap and water is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of dysentery. Communities should promote handwashing practices, especially after using the toilet and before eating.
- Provide Clean Drinking Water: Access to clean drinking water is critical to preventing dysentery. Communities should ensure that all drinking water is properly treated and disinfected to kill bacteria and other pathogens.
- Implement Food Safety Measures: Food can also be a source of dysentery transmission. Communities should implement food safety measures, such as proper food handling, storage, and cooking practices.
- Vaccinate Against Dysentery: Vaccination is an effective way to prevent dysentery. Communities should consider vaccinating against dysentery, especially in areas with high incidence rates.
- Conduct Regular Health Checks: Regular health checks can help identify cases of dysentery early, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further transmission.
- Educate the Community: Educating the community on dysentery prevention and control is critical to preventing the disease. Communities should conduct awareness campaigns to promote good hygiene practices, proper food handling, and safe drinking water practices.
Role of Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers play a critical role in preventing dysentery in post-outbreak areas. They should:
- Provide Medical Care: Healthcare workers should provide medical care to patients with dysentery, including antibiotic treatment and fluid replacement.
- Conduct Contact Tracing: Healthcare workers should conduct contact tracing to identify individuals who have come into contact with a dysentery patient, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further transmission.
- Promote Health Education: Healthcare workers should promote health education and awareness campaigns to promote good hygiene practices and prevent the spread of dysentery.
Role of Community Leaders
Community leaders also play a critical role in preventing dysentery in post-outbreak areas. They should:
- Promote Community Awareness: Community leaders should promote community awareness and education on dysentery prevention and control.
- Mobilize Resources: Community leaders should mobilize resources, such as funding and personnel, to support dysentery prevention and control efforts.
- Support Healthcare Workers: Community leaders should support healthcare workers in their efforts to provide medical care and conduct contact tracing.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is dysentery?
Dysentery is a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening disease caused by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. - How is dysentery spread?
Dysentery is spread through the fecal-oral route, typically through contaminated food or water. - What are the symptoms of dysentery?
The symptoms of dysentery include diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, fever, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, and weight loss. - How can dysentery be prevented?
Dysentery can be prevented by improving sanitation and hygiene, promoting handwashing, providing clean drinking water, implementing food safety measures, vaccinating against dysentery, conducting regular health checks, and educating the community. - What is the role of healthcare workers in preventing dysentery?
Healthcare workers play a critical role in preventing dysentery by providing medical care, conducting contact tracing, and promoting health education and awareness campaigns. - What is the role of community leaders in preventing dysentery?
Community leaders play a critical role in preventing dysentery by promoting community awareness and education, mobilizing resources, and supporting healthcare workers.
Conclusion
Dysentery is a serious public health concern that can have devastating consequences if not prevented and controlled. In post-outbreak areas, preventing the recurrence of dysentery requires a multi-faceted approach that involves both individual and community-level efforts. By improving sanitation and hygiene, promoting handwashing, providing clean drinking water, implementing food safety measures, vaccinating against dysentery, conducting regular health checks, and educating the community, we can prevent dysentery and protect the health and well-being of the affected population. It is critical that healthcare workers and community leaders work together to prevent dysentery and promote a healthy and safe environment for all. By taking a comprehensive and coordinated approach to dysentery prevention and control, we can reduce the incidence of this disease and improve the overall health and well-being of communities around the world.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention in post-outbreak areas. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!