Introduction
Dysentery is a highly contagious and potentially life-threatening infection that can spread rapidly in healthcare settings. The bacterium is typically transmitted through the fecal-oral route, where contaminated food, water, or hands come into contact with the mouth. In healthcare settings, the risk of transmission is heightened due to the presence of vulnerable patients, inadequate hygiene practices, and inadequate sanitation. The consequences of dysentery outbreaks in healthcare settings can be devastating, resulting in significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burdens.
Risk Factors in Healthcare Settings
Several factors contribute to the risk of dysentery transmission in healthcare settings, including:
- Inadequate hand hygiene: Failure to practice proper hand washing and sanitizing techniques among healthcare workers, patients, and visitors.
- Poor sanitation: Inadequate cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, equipment, and patient care areas.
- Contaminated food and water: Consumption of contaminated food and water, particularly in areas with inadequate food handling and preparation practices.
- Patient-to-patient transmission: Direct contact with infected patients or contaminated bodily fluids.
- Healthcare worker-to-patient transmission: Transmission of the bacterium from healthcare workers to patients through contaminated hands or equipment.
Prevention Strategies
To prevent the spread of dysentery in healthcare settings, the following strategies should be implemented:
- Strict hand hygiene: Ensure that all healthcare workers, patients, and visitors practice proper hand washing and sanitizing techniques, using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Proper sanitation: Ensure that all surfaces, equipment, and patient care areas are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected regularly, using a disinfectant that is effective against the bacterium.
- Safe food and water handling: Ensure that food and water are handled and prepared in a safe and hygienic manner, using proper food handling and preparation techniques.
- Patient isolation: Isolate patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery to prevent transmission to other patients and healthcare workers.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Use PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery.
- Staff education and training: Educate and train healthcare workers on dysentery prevention and control measures, including proper hand hygiene, sanitation, and PPE use.
- Surveillance and monitoring: Establish a surveillance system to monitor for dysentery outbreaks and respond promptly to suspected cases.
Infection Control Measures
In addition to prevention strategies, the following infection control measures should be implemented in healthcare settings:
- Contact precautions: Use contact precautions, such as gloves and gowns, when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery.
- Droplet precautions: Use droplet precautions, such as masks, when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery.
- Airborne precautions: Use airborne precautions, such as negative pressure isolation rooms, when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery.
- Cleaning and disinfection: Ensure that all surfaces, equipment, and patient care areas are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected regularly.
- Waste management: Ensure that all waste is disposed of properly, using a sealed bag or container, to prevent the spread of the bacterium.
Role of Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers play a critical role in preventing the spread of dysentery in healthcare settings. They should:
- Practice proper hand hygiene: Ensure that they practice proper hand washing and sanitizing techniques, using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Use PPE: Use PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, when caring for patients with suspected or confirmed dysentery.
- Follow infection control measures: Follow established infection control measures, including contact, droplet, and airborne precautions.
- Report suspected cases: Report suspected cases of dysentery to the infection control team promptly.
- Participate in staff education and training: Participate in staff education and training programs to stay updated on dysentery prevention and control measures.
FAQs
- What is dysentery?
Dysentery is a bacterial infection caused by Shigella, Salmonella, or Campylobacter, characterized by diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. - How is dysentery transmitted?
Dysentery is transmitted through the fecal-oral route, where contaminated food, water, or hands come into contact with the mouth. - What are the symptoms of dysentery?
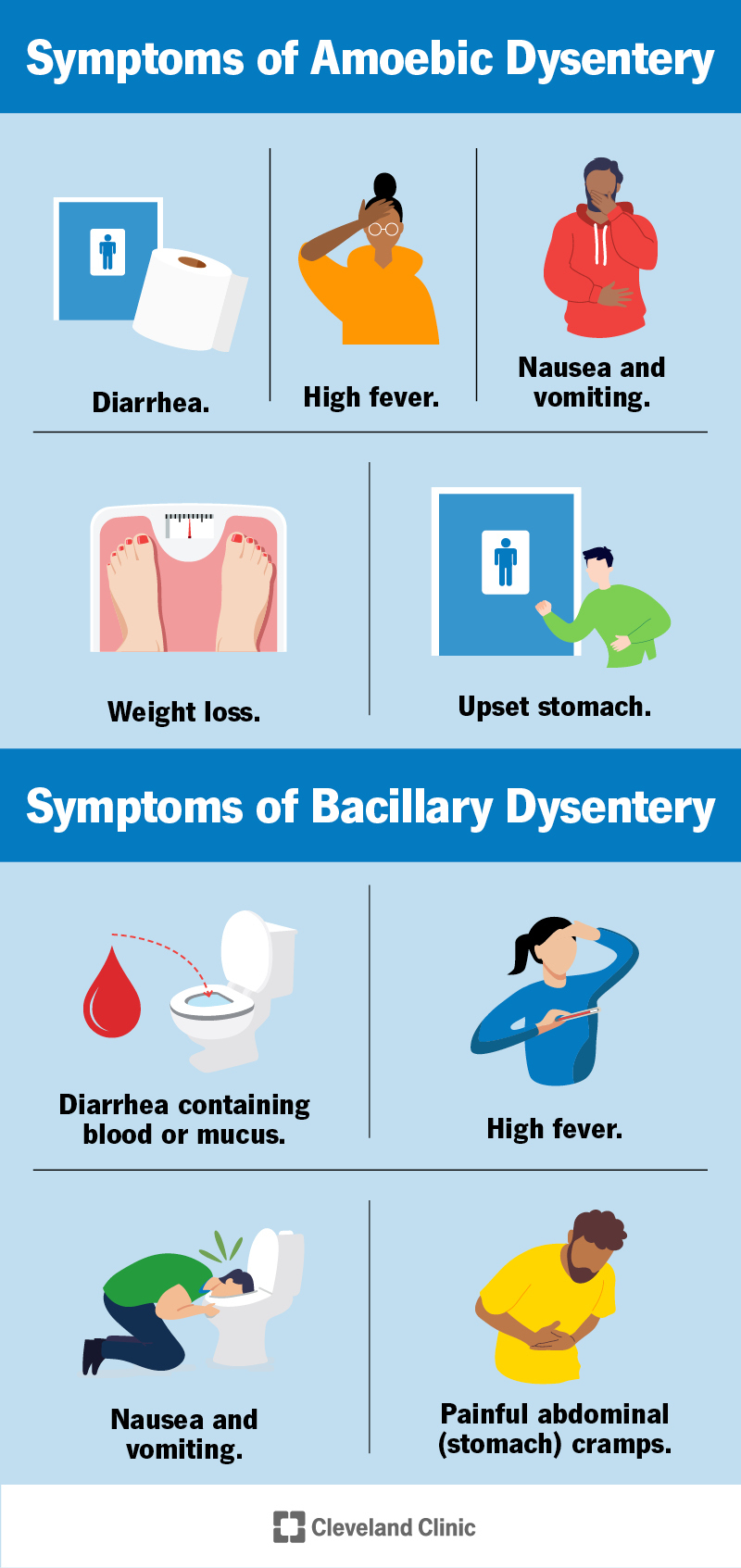
The symptoms of dysentery include diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and blood in the stool. - How can dysentery be prevented?
Dysentery can be prevented through strict hand hygiene, proper sanitation, safe food and water handling, patient isolation, and use of PPE. - What are the consequences of dysentery outbreaks in healthcare settings?
The consequences of dysentery outbreaks in healthcare settings can be devastating, resulting in significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burdens.
Conclusion
Dysentery is a significant public health concern in healthcare settings, posing a threat to patients, healthcare workers, and visitors. To prevent the spread of dysentery, it is essential to implement strict hand hygiene, proper sanitation, safe food and water handling, patient isolation, and use of PPE. Healthcare workers play a critical role in preventing the spread of dysentery, and it is essential that they practice proper hand hygiene, use PPE, and follow established infection control measures. By working together, we can prevent the spread of dysentery and protect the health and well-being of patients, healthcare workers, and visitors in healthcare settings.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention in healthcare settings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!