What is Dysentery?
Dysentery is a type of infectious disease caused by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Shigella, Salmonella, or Campylobacter. The disease is highly contagious and can spread quickly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. There are two types of dysentery: bacillary dysentery, caused by the Shigella bacteria, and amoebic dysentery, caused by the Entamoeba histolytica parasite.
Causes of Dysentery
The primary cause of dysentery is the ingestion of contaminated food or water. The bacteria or parasites that cause dysentery can be found in:
- Contaminated water: Water from wells, rivers, or lakes that are contaminated with human or animal feces can contain the bacteria or parasites that cause dysentery.
- Poor sanitation: In areas with poor sanitation, human feces can contaminate food, water, and the environment, leading to the spread of dysentery.
- Inadequate hygiene: Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands regularly, can contribute to the spread of dysentery.
- Contaminated food: Food that is not cooked properly or is handled by someone with the infection can also spread dysentery.
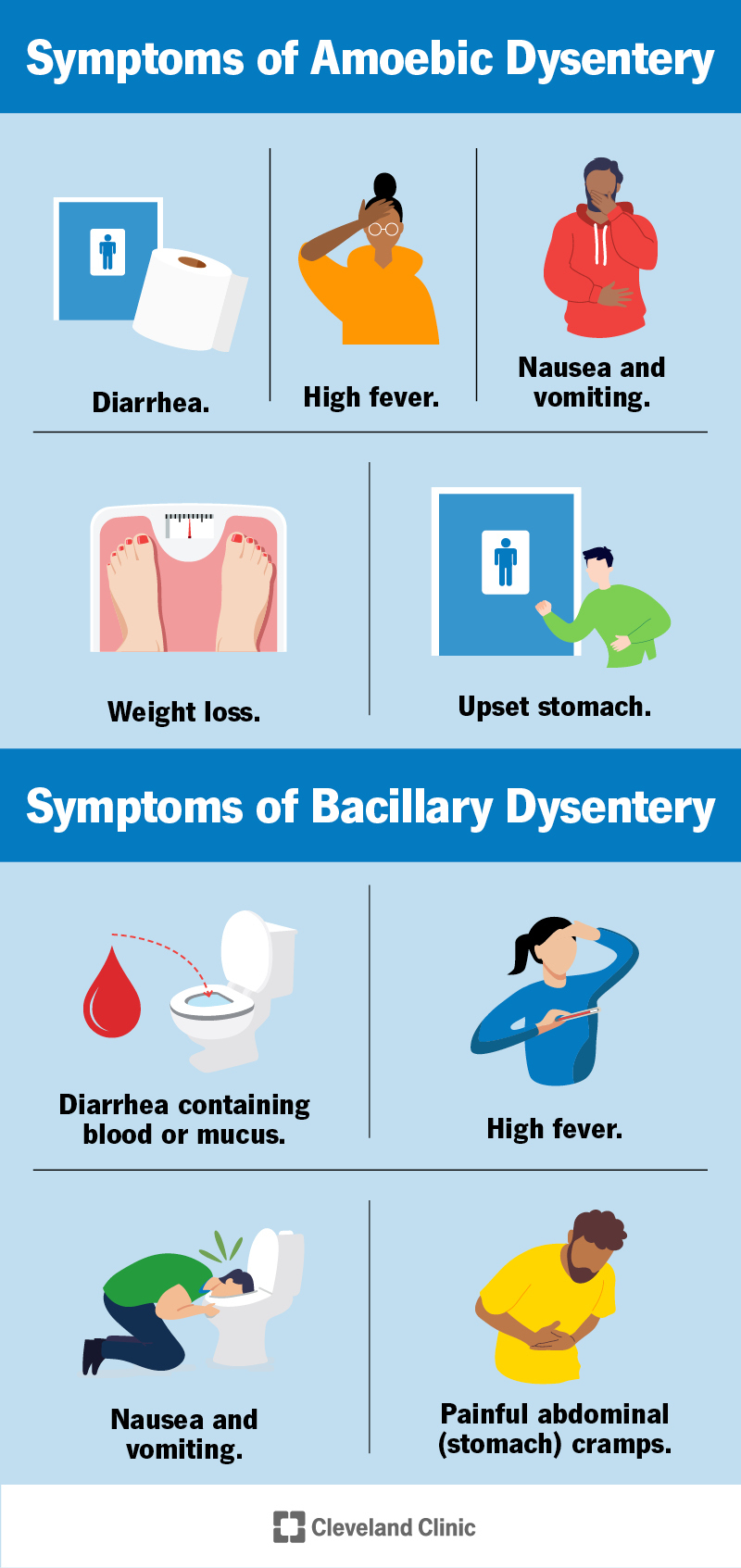
Symptoms of Dysentery
The symptoms of dysentery can vary depending on the type of infection, but common symptoms include:
- Bloody diarrhea: Dysentery is characterized by bloody diarrhea, which can be accompanied by abdominal pain and cramping.
- Abdominal pain: Severe abdominal pain and cramping can occur, especially in the lower abdomen.
- Fever: A high fever can develop, which can be accompanied by chills and sweating.
- Vomiting: Vomiting can occur, especially in severe cases of dysentery.
Dysentery Prevention in High-Risk Areas
Preventing dysentery in high-risk areas requires a multi-faceted approach that involves improving sanitation, hygiene, and access to clean water. Here are some prevention measures that can be taken:
- Improve sanitation: Building proper toilets and sewage systems can help reduce the contamination of water and the environment.
- Promote hygiene: Educating people on the importance of washing their hands regularly, especially after using the toilet and before handling food, can help prevent the spread of dysentery.
- Provide access to clean water: Ensuring that people have access to clean and safe drinking water can reduce the risk of dysentery.
- Cook food properly: Cooking food properly, especially meat and vegetables, can help kill bacteria and parasites that can cause dysentery.
- Avoid close contact: Avoiding close contact with someone who has dysentery can help prevent the spread of the disease.
- Use personal protective equipment: Using personal protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, can help prevent the spread of dysentery in healthcare settings.
- Vaccination: Vaccination against dysentery is available, especially for people traveling to high-risk areas.
FAQs
- Q: What is the most effective way to prevent dysentery?
A: The most effective way to prevent dysentery is to improve sanitation, hygiene, and access to clean water. - Q: Can dysentery be treated?
A: Yes, dysentery can be treated with antibiotics and supportive care, such as fluid replacement and rest. - Q: How long does it take to recover from dysentery?
A: Recovery from dysentery can take several days to a week, depending on the severity of the infection. - Q: Can dysentery be prevented by vaccination?
A: Yes, vaccination against dysentery is available, especially for people traveling to high-risk areas. - Q: What are the complications of dysentery?
A: Complications of dysentery can include dehydration, malnutrition, and even death, especially in severe cases.
Conclusion
Dysentery is a significant public health concern in many parts of the world, particularly in areas with poor sanitation, inadequate hygiene, and limited access to clean water. Preventing dysentery in high-risk areas requires a multi-faceted approach that involves improving sanitation, hygiene, and access to clean water. Education and awareness on the importance of hygiene and sanitation can also play a crucial role in preventing the spread of dysentery. By taking these prevention measures, we can reduce the incidence of dysentery and prevent outbreaks, ultimately saving lives. It is essential to remember that dysentery is a preventable disease, and by working together, we can create a healthier and safer environment for everyone.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention in high-risk areas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!