What is Dysentery?
Dysentery is a type of gastrointestinal infection characterized by severe diarrhea, often with blood and mucus in the stool. It is usually caused by the bacteria Shigella, which can be spread through contaminated food, water, or direct contact with an infected person. The disease can range from mild to severe, with symptoms including abdominal pain, fever, and vomiting.
Causes of Dysentery in Urban Areas
The primary cause of dysentery in urban areas is the contamination of water and food sources. Inadequate waste management, poor sanitation, and insufficient water treatment contribute to the spread of the disease. Other factors that increase the risk of dysentery in urban areas include:
- Inadequate Water Supply: Insufficient access to safe drinking water forces people to rely on contaminated sources, such as rivers, lakes, or wells.
- Poor Sanitation: Inadequate waste management and lack of proper sewage systems allow human waste to contaminate water sources and soil.
- Overcrowding: High population density in urban areas increases the risk of person-to-person transmission of the disease.
- Food Contamination: Inadequate food handling and storage practices can lead to the spread of contaminated food.
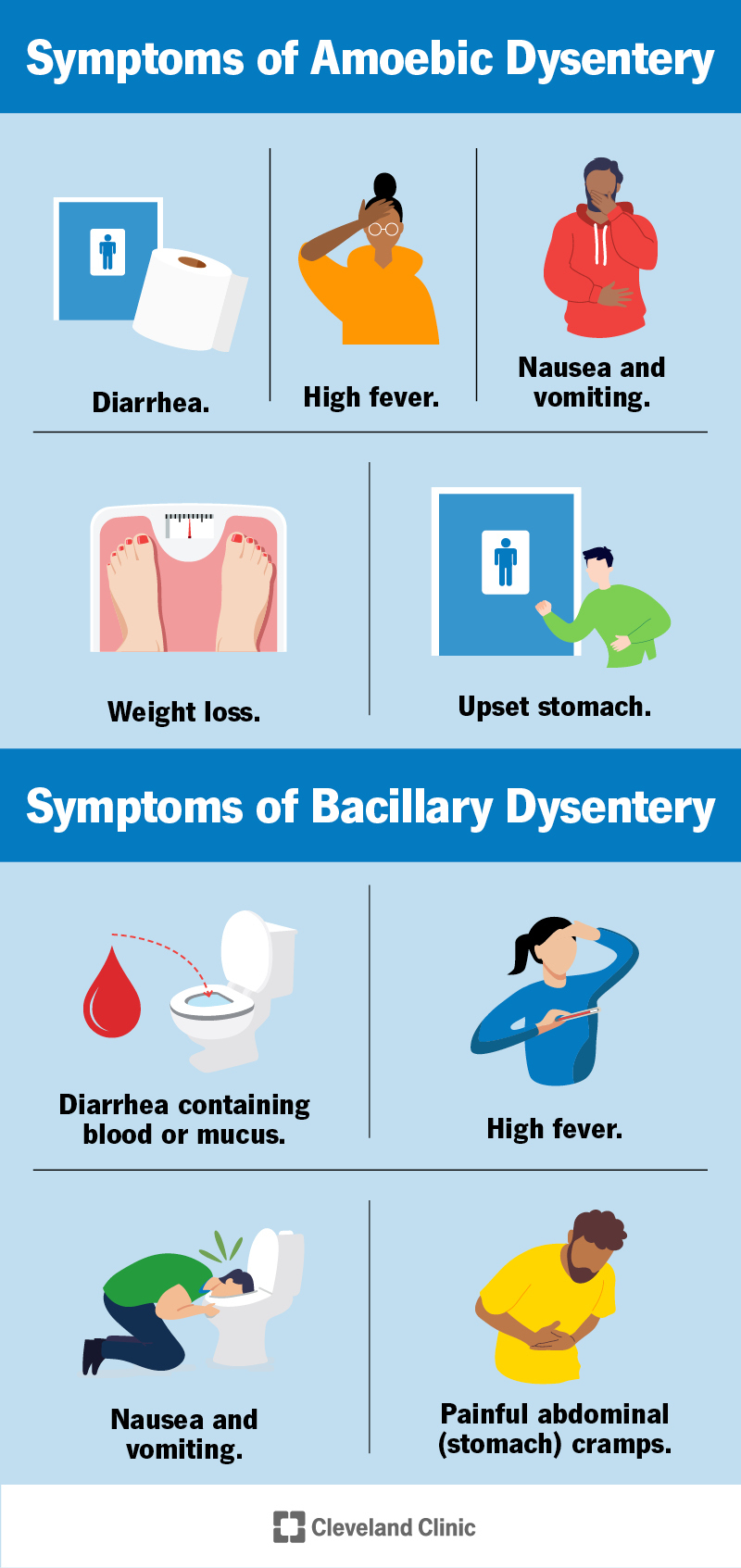
Symptoms of Dysentery
The symptoms of dysentery can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Diarrhea: Severe, watery diarrhea, often with blood and mucus in the stool.
- Abdominal Pain: Severe abdominal cramps and tenderness.
- Fever: High fever, often accompanied by chills.
- Vomiting: Frequent vomiting, which can lead to dehydration.
- Blood in Stool: Presence of blood and mucus in the stool.
Prevention Methods
Preventing dysentery in urban areas requires a multi-faceted approach that involves:
- Improving Water Supply: Ensuring access to safe drinking water through proper water treatment and distribution systems.
- Enhancing Sanitation: Implementing adequate waste management and sewage systems to prevent contamination of water sources and soil.
- Promoting Hygiene: Educating the public on proper hygiene practices, such as handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the toilet and before handling food.
- Food Safety: Implementing proper food handling and storage practices to prevent contamination.
- Vaccination: Vaccinating against Shigella, the bacteria that causes dysentery, although this is not widely available.
Urban Planning and Dysentery Prevention
Urban planning plays a critical role in preventing dysentery in urban areas. Cities can be designed to minimize the risk of disease transmission by:
- Providing Access to Safe Water: Ensuring that all residents have access to safe drinking water.
- Implementing Adequate Sanitation: Building sewage systems and waste management facilities to prevent contamination of water sources and soil.
- Creating Green Spaces: Designing cities with green spaces, such as parks and gardens, to reduce the risk of flooding and improve air quality.
- Promoting Mixed-Use Development: Encouraging mixed-use development to reduce the need for lengthy commutes and promote walking and cycling.
Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives can play a significant role in preventing dysentery in urban areas. These initiatives can include:
- Public Education: Educating the public on proper hygiene practices and the importance of sanitation.
- Community-Led Total Sanitation: Encouraging communities to take ownership of their sanitation and hygiene practices.
- Food Safety Initiatives: Implementing initiatives to improve food handling and storage practices in local markets and food establishments.
- Volunteer Programs: Establishing volunteer programs to promote dysentery prevention and provide support to affected communities.
FAQs
- What is the most effective way to prevent dysentery?
The most effective way to prevent dysentery is to ensure access to safe drinking water, practice proper hygiene, and implement adequate sanitation. - How can I protect myself from dysentery?
You can protect yourself from dysentery by washing your hands frequently with soap and water, avoiding contaminated food and water, and practicing good hygiene. - What are the symptoms of dysentery?
The symptoms of dysentery include severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, vomiting, and blood in stool. - Can dysentery be treated?
Yes, dysentery can be treated with antibiotics, but it is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. - How can cities prevent dysentery outbreaks?
Cities can prevent dysentery outbreaks by providing access to safe water, implementing adequate sanitation, promoting hygiene practices, and implementing food safety initiatives.
Conclusion
Dysentery is a significant public health concern in urban areas, particularly in cities with inadequate sanitation and water infrastructure. However, with a comprehensive approach to prevention, including improving water supply, enhancing sanitation, promoting hygiene, and implementing food safety initiatives, the risk of dysentery can be significantly reduced. Urban planning and community-based initiatives also play a critical role in preventing dysentery outbreaks. By working together, we can create healthier, more resilient cities that are better equipped to prevent the spread of this disease. Remember, prevention is key, and by taking simple steps, such as washing your hands frequently and practicing good hygiene, you can protect yourself and your community from the risk of dysentery.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dysentery prevention in urban areas. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!